Precision Agriculture using IoT Technology: The Future of Precision Farming
The Internet of Things is gathering a ton of buzz in the infrastructure, automotive, and retail industries, among others. What is not so commonly talked about is the IoT’s most important use case yet — precision agriculture. With the food crisis our planet is at risk of entering, these new technological innovations to increase yields could be life-saving.
The efficiency of farming lies in a farmer’s ability to predict natural conditions and react to them in the quickest way possible. A few decades ago, the precision of such forecasts wasn’t so reliable — now, it’s impressively high thanks to instant data gathering and distribution.
The Internet of Things is successfully fueling precision agriculture as a new direction in farming. In this post, you’ll find out more about what it is, the IoT technologies used to improve the quality of data gathering, and their applications in the field.
Technological advancements allow both small and large-scale agricultural businesses to implement precision agriculture. It is only now becoming widespread in this decade — yet, the origins of this trend can be traced back to the 90s. Back then, GPS-satellite adoption allowed farmers to gather datum and steer agriculture equipment automatically.
Now, there are more technologies that allow farmers to gather more precise data — sensors, aerial devices, stationary IoT solutions for precision agriculture, and so on. To answer the question ‘What is precision farming technology?’ in more detail, let’s look at the major objectives of using this approach.
- Gather farming data, including historical, predictive modeling and environmental insights to choose suitable crops with higher yields
- Measure the performance of the site by capturing data in real-time
- Use digital farming data (soil, crop health, weather, etc.) to provide the exact amount or water, nutrition and optimize pest control
- Increase the farm’s economic and environmental sustainability
- Predict weather changes and react to them proactively

Precision agriculture reduces crop waste along with the negative impact on the environment. It allows farmers to get as much yield as possible out of each site. That’s why researchers consider precision agriculture an efficient way to solve food crises all over the world.
Looking for an agriculture software development company? Let’s talk!
Contact Digiteum
As for now, farmers are coming to recognize the advantages brought by precision farming using IoT. Agriculture business owners see incorporating technology into crop and cattle management as a way to improve the quality of decision-making, the return on investment (ROI), as well as the overall site security.
More metrics for agriculture monitoring
Thanks to digital tools, a grower will be able to continuously monitor a wide range of metrics — including rainfall levels, the number and the nature of nutrients that crops need to grow to a peak level, soil samples, fertilizer inputs, and so on. A deeper insight into the state of crops helps farmers make informed decisions across all fields.
Improved decision-making efficiency
When farmers adopt the use of precision agriculture sensors to monitor the soil moisture, crop health and nutrition levels, they get long-term access to valuable real-time data. This way, a site manager will be able to distinguish patterns and predict changes, potential risks, and yields, both through harvest and the growing season.
Access to farm records
Using technology for farm management increases data accessibility. With precision agriculture, the team members are no longer bound to the office space. Thanks to cloud-based technologies, all the necessary data is free for access any time from any device.
Better crop protection

The excessive use of chemicals is one of the causes of high crop and soil pressure. To protect the site from crop-damaging insects, farmers tend to go overboard with their nitrogen usage. Apart from reducing the environmental sustainability of the site, using chemicals is expensive. One of the biggest benefits of adopting precision agriculture using Internet of Things is to optimize pest control and use chemicals only when needed and protect crops more efficiently.
Irrigation management

Agriculture accounts for over 70% of water usage across the world, according to OECD. As the world is experiencing drinking water shortages, careful distribution at farming sites is imperative.
By adopting centralized command-and-control tools, farming teams can tell precisely when to irrigate a given field. As a result, crops are preserved in a better state and the management framework is socially responsible.
These are the benefits of precision agriculture in IoT for modern farming landscape. As the approach has an extensive list of advantages, it’s certainly worth implementing.
The meaning of precision agriculture by default implies the heavy use of technologies, and most advancements used here are closely connected with the Internet of Things. Here’s a closer look at the technologies that are effective for precision farming using Internet of Things:
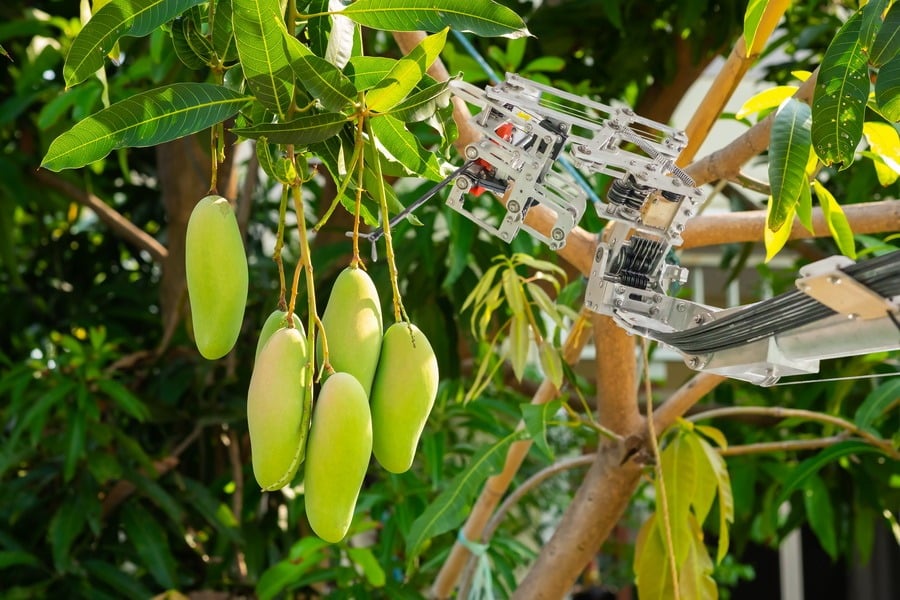

- Sensors. They have the capacity to detect a range of biomolecular, chemical, optical, thermal, electrical, radiation, and biological metrics to get a 360-degree view on the health of crops. By mounting health monitoring sensors on animals, farmers can track the state of livestock in real time.
- Precision farming software. Controller tools are widely used in IoT-based precision agriculture technology. IoT improves software maintenance (e.g. automatic equipment updates) and introduces new solutions for farm management (managing a safe-driving tractor remotely via a controller). The capacity of modern precision agriculture and IoT allows controlling dozens of equipment units simultaneously.
- Connectivity protocols. While a fair share of network protocols work efficiently on short rangers (ZigBee or Wi-Fi), it’s the long-range ones that are the most beneficial for precision agriculture. The most widely used connectivity protocols used by intelligent farming are cellular connection, LoRaWAN, LPWAN, and a few others.
- Location monitoring tools. Satellites are widely used to estimate the amount of water in the soil, crop biomass, and many other metrics. The data collected by connected GPS satellites or a location monitoring solution is then used by crop insurance companies, governments, scientists, policymakers, and commodity bodies.
Thanks to these technologies, farmers can expect enhanced precision in data gathering and analysis, monitor all crop farming activities and performance, and get a big-picture view of farm sites.
To get a clear view of the potential of the Internet of Things in agriculture, let’s take a look at the benefits of implementing Internet of Things in precision farming.
Insights on the state of the farm
A farmer will be getting a multifaceted analysis of all the processes you’re overseeing — crop and cattle management, weather conditions, the quality of soil, staff’s performance, and so on. All of these records will be stored together and easily accessible — they’ll form a cohesive picture of the site’s progress and development.
Learn more
Reduced resource waste
The Internet of Things in farming reduces operating costs and production risks. By accurately estimating the yield volumes that’ll be harvested at each field, you’ll be able to build smarter distribution strategies and outline potential revenue streams beforehand.
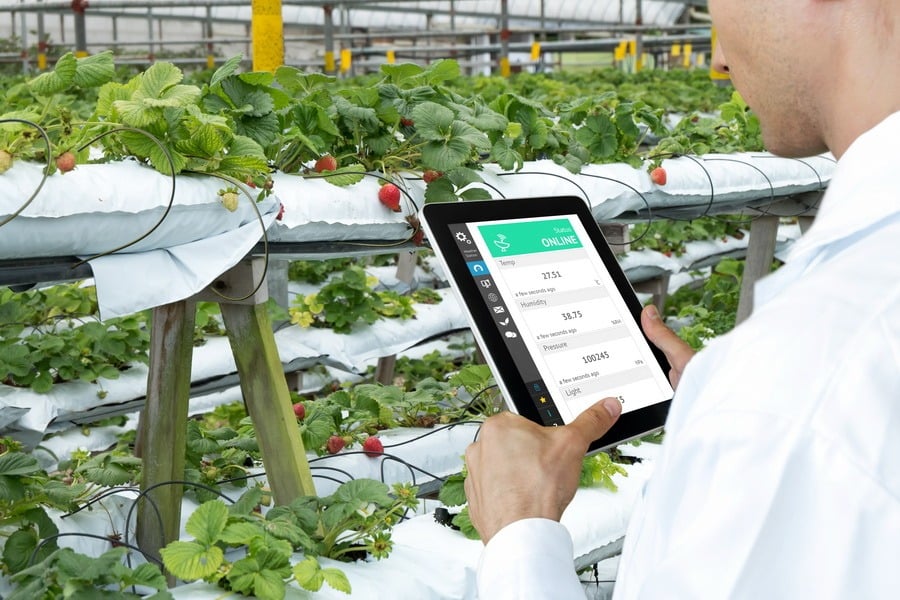

Identifying developing patterns and trends
By getting insights on all kinds of crops, across all fields during the entire season, a site manager will eventually be able to determine which risks or natural conditions are likely to repeat the next year. By analyzing the yield by crop type, farmers will be able to predict which will be lucrative in the years to come.
Getting advanced field data from connected UAVs
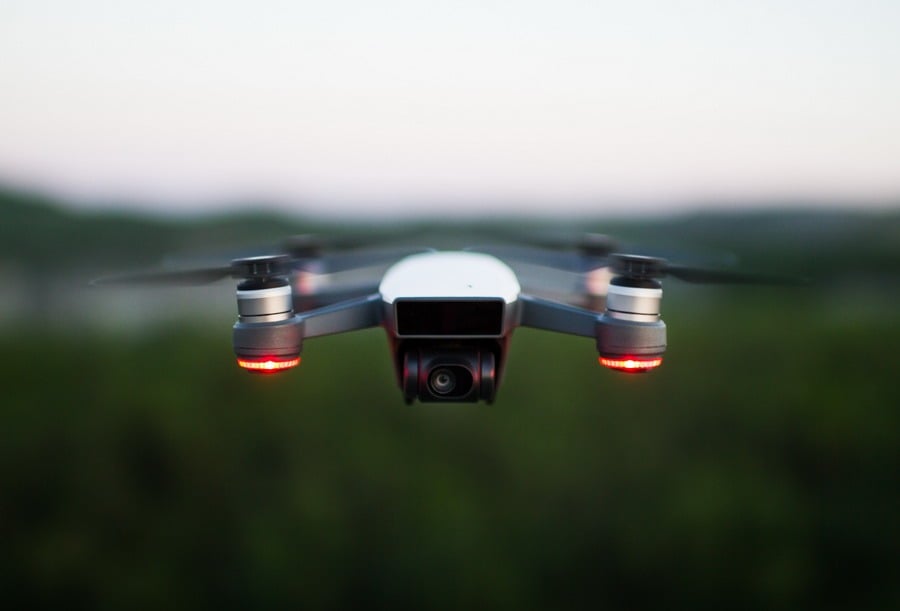

Unmanned aerial vehicles (known to the public as drones) fitted with hyperspectral and multispectral sensors help farmers determine the health of plant leaves and measure water stress levels. Other than that, UAVs also contribute to disaster management and risk reduction.
Contact Digiteum
Better control over internal processes
Using IoT monitoring technologies, site managers can update farmers regarding the state of the field in real time, track their performance, and exchange insights and approaches that teams in separate fields use.
IoT for precision agriculture improves the farm, field, and cattle monitoring; risk management; and planning. It covers nearly all facets of running an agricultural enterprise and has a wide range of cheaper and more ambitious technologies to offer.
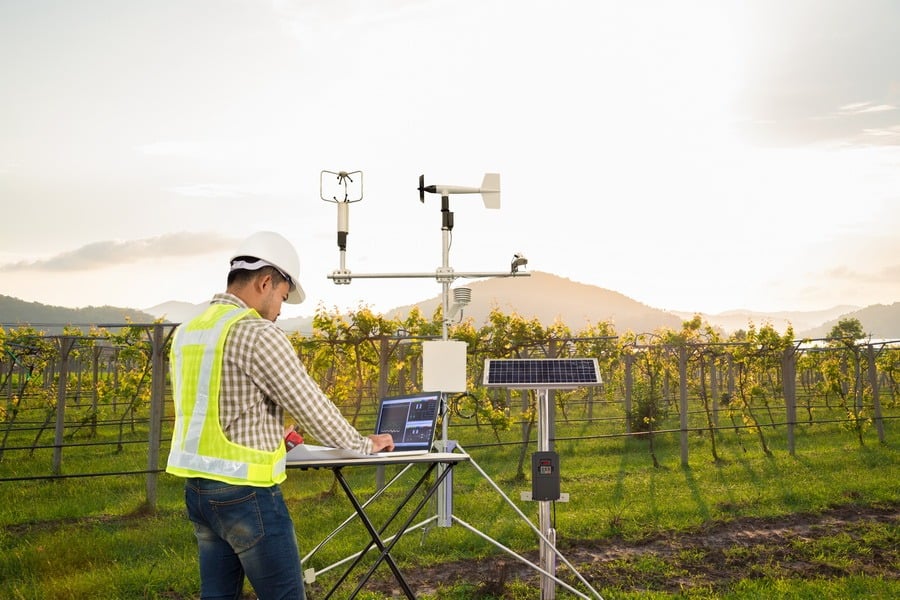

Depending on the focus on the farm, potential Internet of Things use cases will likely vary. These are some of the most popular types of precision farming systems:
- Climate monitoring. Weather stations equipped with farming stations help farmers track and predict weather conditions in a needed area. After having collected insights from the environment, connected devices send the data to cloud-based storage. From there, farm managers can use the information for climate mapping and crop selection.
- Crop monitoring. Crop management devices are a crucial component for using precision Ag technology efficiently. These devices are typically placed on the field — they will monitor water levels, crop health, and other relevant biochemical and physical properties. Using crop monitoring tools, a farmer can proactively manage anomalies, build prediction-based models and strategies, and prevent potentially harmful diseases.
- Cattle monitoring. Sensors are even more important for animal management than they are for crop maintenance. For one thing, they can serve as location trackers so that a part of the livestock is not lost. Also, farm manager will be getting real-time insights on whether cows, pigs, and other farm animals are not sick or hungry. Connected collar tags are the most widespread form of devices for cattle monitoring. They cause no stress for the animal, all the while providing farmers with real-time insights.
- Greenhouse automation. Delegating greenhouse management to an IoT platform for precision agriculture, many activities and processes in the greenhouse can be fully automated. For instance, humidity, temperature and lighting control can be done automatically. Even soil or nutrient solution administration within the greenhouse can be managed with no human supervision thanks to precision agriculture systems.
These are some of the most widely used and efficient examples of using IoT for precision farming. They are not too expensive to develop, easy to maintain and offer an impressive amount of insight.
As there’s more than enough interest in IoT implementation at farms, it’s no wonder there’s no lack of impressive innovations either. In case you’re wondering how far the Internet of Things has come, here’s a list of impressive farming inventions:
Global positioning systems

A GPS is not a new invention nor it is limited to agriculture only. Nevertheless, its impact on farming is undeniable — from tracking field operations to scanning the position of your equipment and livestock. It’s safe to say that the invention of the Global Positioning System has laid the foundation of modern-day precision agricultur and still is one of the most widely used field management and precision farming technologies.
Yield monitors
This invention, originating in the mid-nineties, helps farm managers quantify yield variations across the field and determine the catalysts for such (soil fertility, weather, differences in crop management, and so on). Yield monitors are empowered by GPS and sensors to offer deep insights.
Automated planter controls
The technology gives site managers remote control over the planting process. Dedicated systems will automatically enable and disable planters if crops have already been sown in certain areas. The technology improves planting efficiency, reduces the time needed to finish the process and the amount of wasted seed.
GIS software
GIS systems give farmers a possibility to aggregate data in a visually-rich way. By generating custom color-coded maps, the tool gives a full view on soil condition, crop fertility, insect, or disease pressure. The insights, collected by a GIS tool are pressures as they offer data that would not be spotted with the naked eye.
Irrigation control systems
Thanks to the growth of precision agriculture using IoT, irrigation monitoring has come a long way. Now, dedicated systems can fully handle irrigation, send real-time alerts to a manager in case of anomalies, distribute the exact amount of water a given type of crops needs. As a result, a site manager reduces the amount of workforce as well as water and energy waste.
Conclusion
Precision agriculture is an approach to farming that employs data sensors, connected devices, remote control tools, and other advanced technologies to give farmers more control over the field and the team.
As a result, an agriculture company manager or farmer will be able to adapt to and predict environmental changes, reduce risks when creating distribution strategies, and make informed decisions.
If you are working on an IoT project and looking for skilled Internet of Things software developers, drop us a line. At Digiteum, we design and develop software of any complexity and scale and help small and large businesses integrate innovative technologies, evolve and win the market.
Go to our portfolio to see Digiteum’s latest project and leave a message to discuss how we could help you create and launch your agricultural software.
Contact Digiteum
FAQ
- Get access to insights on the state of the farm and real-time monitoring.
- Reduce resource waste.
- Identify patterns and trends.
- Get a big-picture view using different sets of data (field sensors, UAVs, satellite, etc.)