How to Build an IoT-based Irrigation System for Smart Agriculture
Smart agriculture is a solution to many global agricultural issues, like increasing team productivity, monitoring results, communicating with other teams and sub-units, as well as controlling market tendencies. All over the world, farms are rapidly looking into adopting IoT solutions into their workflows. By 2023, the global IoT agriculture market is predicted to reach $30 billion.
Farmers have already been actively exploring high-tech solutions in their daily work — for example, they use sensors to create detailed maps of the farm area and to analyze the characteristics of the soil. Smartphones are used to monitor productivity, crop growth, and obtain information on market changes. IoT provides an opportunity to connect all these innovations.

Table of Contents
- How To Build An Irrigation System For Farms
- Types of Farm Irrigation Systems
- The Role of IoT in Agricultural Irrigation
- 5 Steps to Build Your Own Irrigation System
- Examples of Irrigation System for Agriculture
- IoT Irrigation System Solution with Digiteum
How To Build An Irrigation System For Farms
For the majority of farms, use of IoT in agriculture begins with smart irrigation. Optimizing the schedule and amount of water allows us to save resources and provide the best care for crops. Sensor-based IoT technologies collect data about soil and update a crop status and transmit this information from sensors to farm irrigation systems. As soon as there is not enough water in the soil, a platform reacts to this alert and the water sprinkler turns on.
Smart irrigation is based on flow pressure and temperature updates — as soon as the moisture has reached a specific threshold, the irrigation will stop. An end-user can track the pump status, making sure that a pipe is in working conditions and the water is flowing in proper amounts.
Learn about software development for agriculture with Digiteum
Automated irrigation systems allow users to track their irrigation status, start and finish the process with a press of a single button, and receive updates on moisture levels, weather updates, and crop status. To serve these multiple objectives, a system should be equipped with six main features:
Remote control
Agricultural irrigation systems are typically navigated via a smartphone or laptop. A user downloads a mobile app that enters profile credentials and gets redirected to the management page. Some farms prefer to develop an additional physical device to control irrigation, seeing how smartphones can be hacked rather easily.
The remote, be it a smartphone or physical device, is connected to sensors that collect and communicate the data on the moisture levels, temperature, and soil status.
Precision agriculture
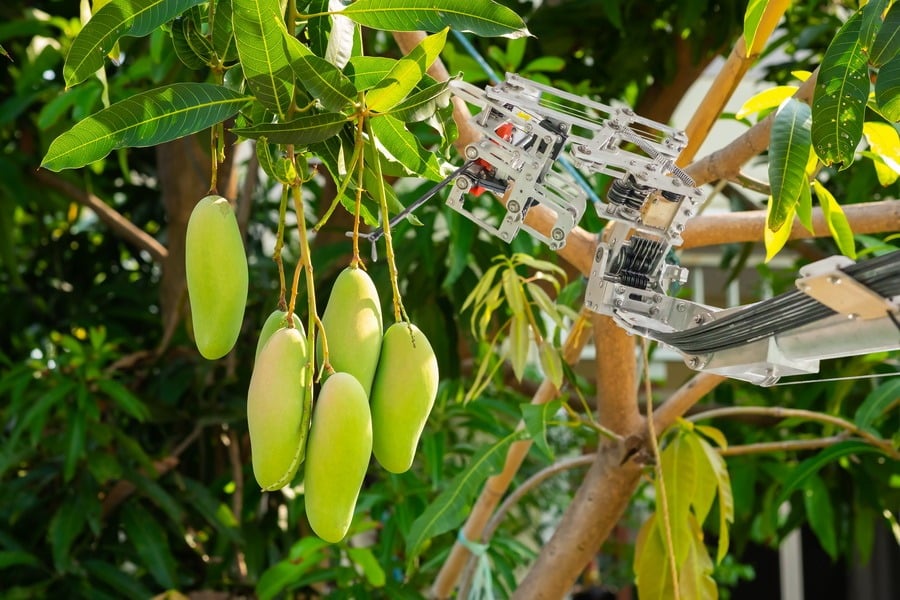

Different crops have specific irrigation schedules according to their biological needs. Precision agriculture using IoT and advanced analytics technologies allows to plan and implement farming activities such as irrigation or pesticide management on-demand depending on the current soil and crop conditions.
To make sure that each type of plant receives the best care, the irrigation system should recognize various zones depending on the sort of crop, soil, and weather conditions. Farmers should be able to set a separate schedule for each of these areas depending on the real-time sensor reads and install a separate irrigation valve for each of them.
Smart schedules
Smart irrigation systems vary by their levels of complexity, especially when it comes to watering customization. Some tools allow setting basic timing for a particular irrigation zone with a possibility to pause or finish the irrigation at any given moment. Other systems support complex schedules in weekly advance with planned breaks and intensity variations. Meanwhile, a water management system using IoT sensors is be able to adjust the watering schedule and intensity based on the reading from moisture, humidity and other sensors.
Notification systems
The system should notify the farmer about the start of watering and its finish, as well as send error alerts. If there is a technical problem, the system should be able to detect abnormalities in the irrigation flow and notify the farmer immediately.
Weather and environment analytics
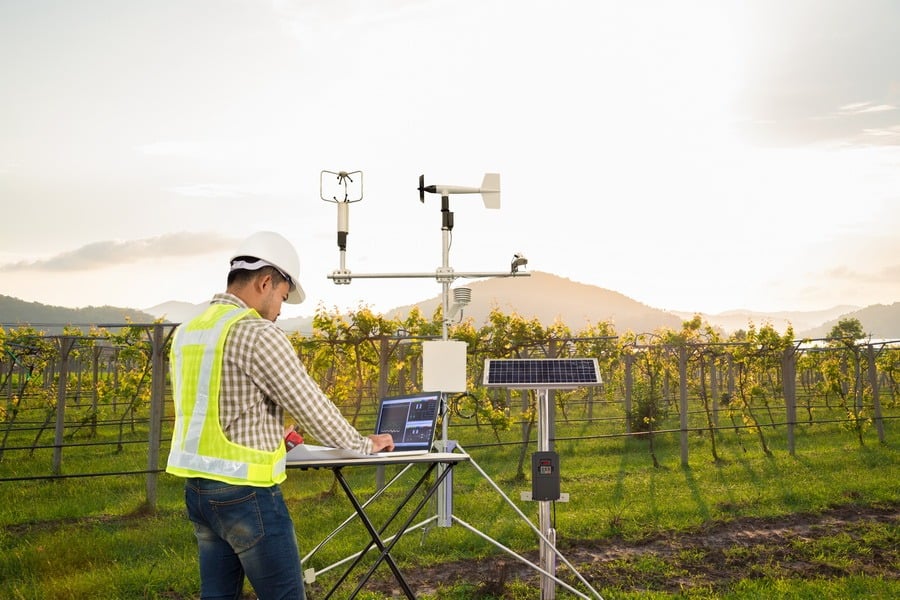

Advanced systems rely not only on the levels of moisture in the soil but also take into account the field location and specifics, as well as the current weather and the forecast. Based on the forecast and machine-learning predictions, the system is able to create customized long-term irrigation schedules.
Interoperability
Field irrigation systems should connect to other smartphones and laptops. The idea behind this connectivity is that a farmer should receive updates any time and from any available device.
Types of Irrigation Systems For Farms
The specifics of the implementing smart irrigation heavily depend on a particular type of irrigation, as it changes the watering techniques and presents unique challenges. There are four common types of irrigation systems, and each of them can be connected to an IoT controller.
1. Flood irrigation

Flood irrigation is the type of irrigation where the water is directed either by furrows (furrow irrigation) or by a strip of a field separated from the rest of the territory by Earth borders (graded border irrigation). Water is supplied from an underground pipe.
2. Sprinkler irrigation

Sprinkler irrigation is a more universal type of irrigation because it doesn’t require a particular channel or furrow. There are several types of sprinkler innovations.
- Hand move pipe — the sprinkler is attached to PVC pipes which are installed in a row around the field. Usually, these pipes are located at a 40-foot distance from one another.
- Solid set — the PVC pipe is permanently stationed underground through the territory of the entire field. The sprinkler is installed on the field’s surface.
- Mechanical Move Systems — the sprinklers are installed above the crop.
- Traveling Gun irrigation — the sprinkler is attached to a tractor and it irrigates the field as the machine moves along.
Sprinkler irrigation is the most common type for implementing IoT. The sensors are connected to the field and the sprinkler so that the sprinkler can receive data from the field.
3. Drip irrigation
This type of irrigation is used often for small fields and consists of small-radius emitters. Such irrigation directs water directly to the roots of the crops, optimizing water expenses. It’s used in garden farming and for vegetable crops, and less applied on corn or cotton fields.
4. Micro-irrigation
This is the most precise type of irrigation since micro-irrigation uses low-volume sprinklers. These are used for vineyards and orchards — mainly because these types of farms require precise control of watering magnitude and schedules.
Hence, the automation of such irrigation should prioritize precision and thoroughly track the data, obtained from sensors. It’s also crucial that a tool can track even the slightest variations in the moisture threshold and stop watering whenever the field is approaching critical levels.
The Role of IoT in Agricultural Irrigation

Agriculture and irrigation practices hugely depend on the type of crop and environment and require precise control. This is why using IoT in irrigation and other smart technologies for watering management has been a priority for farmers for several years. IoT sensors can provide real-time updates on even the smallest fluctuation of moisture and subtle weather changes, altering the irrigation schedule.
Managing water expenses
Water is the most crucial factor of the harvest’s quality and health. Irrigation management controls the amount of used water and ensures that the crops receive the right dosage at the specific timeframe. The Internet of Things makes monitoring more accessible by connecting sensors and collecting all data on the smartphone or laptop.
Make your agriculture practices more efficient, sustainable and profitable
Leverage our experience in custom agritech development to design and built digital tools that help you work smarter and grow more.
Show agritech development servicesPreventing water waste
The lack of prompt monitoring and careful supervision leads to a waste of irrigation water. This harms crop health, damages the soil, and can lead to drought. Smart irrigation software preserves water resources by using exactly as much water as needed by the crop.
Efficient crop yield

The demand for agricultural resources is getting higher as the population continues to grow. To meet this rising request for food, farmers have to optimize their working processes and resource management to be able to produce more crops in a shorter time. IoT analytics provides real-time updates, notifies about market opportunities and threats, and allows tracking environmental conditions (humidity, rainfall, temperature, etc).
6 Steps to Build Your Own Drip Irrigation System
Smart irrigation should provide the possibility to customize the schedule for crop irrigation, decreasing water waste, and evaluate dampness levels. This is achieved with a microcontroller that acts as a channel for information transmission. The microcontroller is connected to sensors that transmit data on moisture, temperature, etc. The following five key steps will show you how to build an irrigation system a simple way:
Step 1. Prepare hardware
For an irrigation system, you need to have the following farm irrigation equipment:
- Soil moisture sensors for analyzing the dielectric data of soils for analyzing water levels and volumes;
- SMS controllers for scheduling on-demand irrigation;
- Temperature sensors, equipped by RTDs — Resistance Temperature Detector Components.
Step 2. Set up LED lights
The LED light can automatically turn on to notify the farmer about changes of moisture and temperature, as well as alert the entire irrigation system. LED bulbs are used to monitor the status of water sprinklers in different field zones.
Step 3. Substituting static sprinklers with rotating nozzles

The usage of rotating nozzles on the water sprinkle can minimize the water waste — it will send precise water currents into many zones. The variation of rotation angles allows sprinklers to get access to all areas of the land.
Step 4. Internet connection
IoT systems transmit information by using wireless networks, connected to the regulator and other devices. Firstly, sensor data are transmitted to data processing center via a low-power network — typical options are Sigfox and LoRaWAN. The next step is to send data insights to farmer’s dashboards on a laptop/mobile, using these devices as controllers.
Step 5. Locating sensors
Sensors should communicate real-time data to the cloud (or other data storing and processing centers) about soil surface status. They should be located in the zones that represent well the overall condition of the soil — usually, near the root of the plant. The sensor should be protected by soil to avoid direct contact with water.
You can use drones for additional assistance to help monitor large fields many miles away and figure out the areas that need watering on demand.
Step 6. Monitoring technical issues
Cracks and tank leaks are common problems of many irrigation systems. Hence, it’s crucial to build a drip irrigation system with leakage control. The sensors should detect abnormal water flow and send alerts to the entire system. The notifications algorithms immediately notify the farmer. Also, as soon as the moisture levels are above the maximally allowed threshold, the irrigation should cease automatically, even if the farmer doesn’t stop it manually. Hence, automation algorithms are essential for the successful prevention of irrigation risks.
Examples of Irrigation System for Agriculture

The smart irrigation market has been rapidly growing during the last 5-10 years, and industry leaders have presented cutting-edge irrigation solutions for farms of different sizes and crops. Let’s take a look at the most prominent providers of smart irrigation services.
Hunter Industries
Image credit: Hunter Industries
The company offers three main irrigation systems for small and big farms that differ by types and number of used controllers.
- IMMS is a central water management software for Windows that supports 10,000+ controllers. The platform’s essential functionality is flow reporting and control with ACC controllers, irrigation statistics, and alerts, as well as the support of wireless Ethernet and GPRS protocols. The system is compatible with Solar Sync sensors for temperature and sunlight analysis.
- Hydrawise Cloud platform is a mobile water management application, available on iOS, Android, and Windows Phone. The solution supports an unlimited number of controllers. The app allows farmers to access multiple controllers simultaneously and uses predictive algorithms to forecast the necessary water expenses based on weather forecasts.
Calsense
Image credit: Calsense
Calsense developed an online and mobile platform for IoT irrigation management, using CS3000 controllers and real-time moisture sensors. The platform notifies the farmer about mainline breaks and real-time weather updates. The web application also compiles real-time irrigation dashboards and connects a farmer to the cloud storage, where all reports are stored and encrypted.
Galcon

Image credit: Galcon
This irrigation helps farmers who are using the Internet of Things communicate data from sensors to the DC controller both offline and online. Even without an Internet connection, a farmer can track irrigation status, schedule new activities, modify flow intensity, and monitor water consumption statistics.
The data is protected by individual passwords — each user has a personalized admin panel. Cloud storage provides seamless data access from desktop and mobile devices and doesn’t require hard drive storage.
IoT Irrigation System Solution with Digiteum
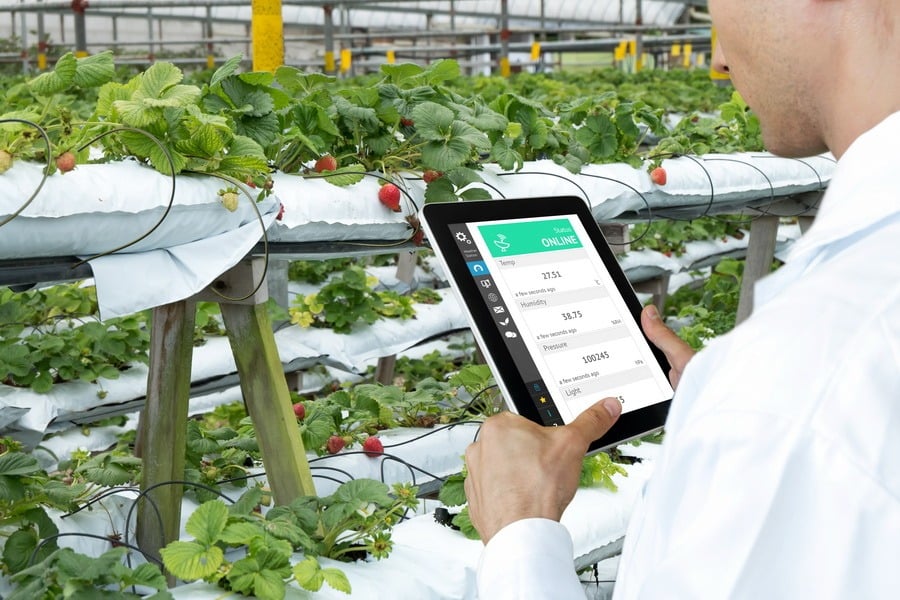

Smart irrigation is an innovative approach to watering, enabled by connected sensors, devices, and remote controllers. Farmers and their employees get a real-time outlook on the irrigation process and can automate their workflow.
Ultimately, the farm manager can predict possible threats, base irrigation schedule on weather updates and moisture levels, and use statistics from previous irrigation sessions. The process of farming leads to less waste and is more predictable — farmers can rely on their previous experience to adjust to changes and build a future farming strategy.
The development of a smart irrigation system requires an expected IoT development partner who understands the specifics of working in the industry and the stakes of even a single error. At Digiteum, we have experience in software development for agriculture and a wide skillset for IoT software development.
As an IoT application development company, we can help you design and build an efficient irrigation management platform. Take a look at our latest IoT projects and drop us a line to get an estimate for your custom irrigation software.
Start or scale your agritech project
Equip your business with digital tools to optimize the use of resources, minimize waste and maintain reasonable cost balance.
Start my project