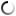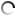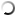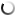The Role of Internet of Things (IoT) in Smart Grid Technology and Applications
As the traditional grid system is aging and barely keeps up with the growing electricity demand, governments around the world focus on adopting and integrating smart grid technology.
It has been in focus in the European Union as a system to “efficiently deliver sustainable, economic and secure electricity supplies” for years. In the United States, the efforts for shifting towards smart and clean energy have started a decade ago when the country established the first policy in this direction. From this point, the investment, technology research and development for the smart grid were officially supported by the U.S. government.
In this article, we’ll find out what makes smart grid so important at the national and global level, how it works and how IoT is used in smart grid system development.
Here is one smart grid definition that covers all important aspects and doesn’t go into many details:
It’s an electricity network that consists of a system of infrastructural, hardware and software solutions that enable two-way communication between all system parts and participants and provide efficient power generation and distribution in the supply chain.
Smart grid is often characterized as a self-sufficient distributed system. It can provide energy from different power sources, including renewables and storage. Moreover, the implementation of this system enables suppliers and consumers with unprecedented control and management capabilities.
You can find a more detailed explanation in Techopedia. Now let’s move on to see how smart grid technology works.
Contact Digiteum
Unlike a traditional grid with one-way communication, a smart grid is a complex network that implies multiple two-way interactions between equipment and participants in the supply chain. This structure enables various scenarios of how generated power can move and be managed. Here’s the most basic step-by-step scenario.
1. Generate
Switch to the smart grid allows using the power generated from different and often distributed sources. It includes traditional power plants, renewable solar and wind as well as plug-in electric vehicles and energy storage.
Read: Benefits of using IoT in oil and gas industry
2. Distribute

Using a network of transmission lines, substations and automated distribution systems, the power is transformed to the correct voltage range if needed (in case of solar or wind) and distributed among the end-users.
3. Use
End-users get broad power management capabilities and visibility thanks to smart grids IoT applications such as smart meters, sensor-enabled appliances, smart sockets, plugs, etc. Using these tools, consumers become active participants in managing their electricity consumption — use mobile or web apps to monitor and remotely control power usage, configure automated regimes, respond to load changes and control their spending and emission in real time.
Read: Benefits of using IoT in water management
4. Control
People, utility companies and other professionals in the energy industry expand their control and management capabilities in a smart grid. Connected homes, communities and the whole cities use electricity and create data on the consumption and loads. This data can be used by any authorized participant in the supply chain. Thanks to data analytics and visualization tools, energy consumption data is turned into insights that make the basis for future decisions.
For example, energy companies can manage grid assets and perform predictive maintenance, utility companies can build demand response programs, residents can dynamically respond to the difference in loads and cut on the consumption when energy is the most expensive.
5. Store
Not only do households practice a more prudent energy use, but also store enough power to provide a house in the off-grid scenario. Using storage, households save extra energy, choose the loads they need to back up and use this energy in the case of an outage, for example. Apart from giving management benefits, storage becomes one of the innovative smart grid technologies essential for independent residential grids that fully rely on renewables and generate much surplus.
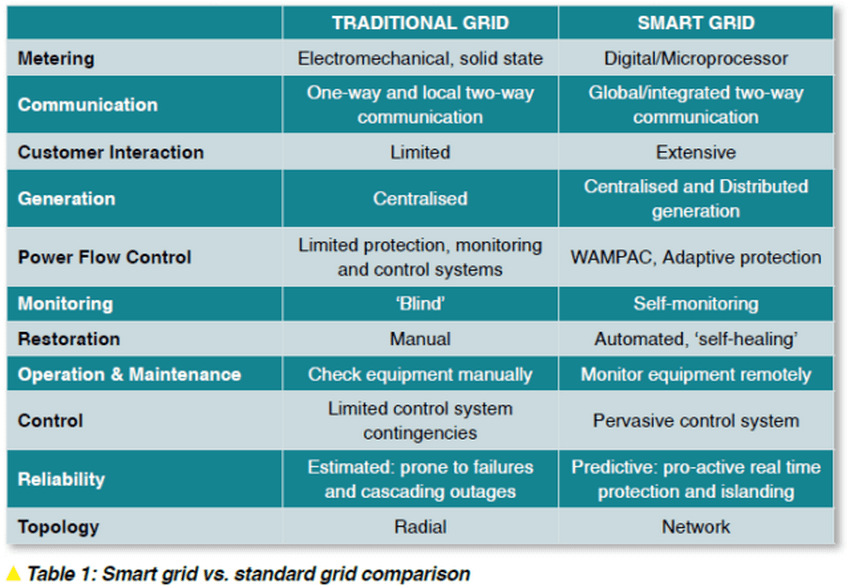
Traditional grids are aging and no longer effective with respect to growing electricity demand. The image below proves it showing the basic differences and benefits of a smart grid over a traditional one. Apart from these advantages, there are three basic reasons why we need smart grid technology and applications.
To cut cost and risks
Among the biggest problems smart grid solves are wasted resources and lack of safety. Adoption of smart grid technology by households and the whole cities helps monitor and control energy use in real time and optimize it with the best interests of citizens and the environment in mind.
At the same time, improved visibility of every grid’s element — loads, equipment, transmission lines, appliances — allows management to detect any problem in time or even in advance, address it accordingly and prevent expensive and dangerous problems like outages and downtime due to untimely maintenance.
According to the Department of Energy, outages cost Americans $150 billion yearly.
To reduce emissions and carbon-heavy electricity

Not only does an IoT-based smart grid system provide intelligence, visibility, control and communication into the energy consumption process. Smart grid enables green energy adoption at a wider scale.
First of all, together with reduced wasted energy come reduced emissions. Secondly, smart grid architecture allows including renewables into the network, which makes clean energy sources more accessible for people.
To provide resilience
Today, smart grid software enables consumer-level monitoring and control of energy consumption. It makes a household resident an active participant in the grid’s lifecycle, and a decision-maker too.
Using technologies like energy storage or PV systems, a household can temporarily go off-grid, for example, in a case of maintenance or accidents on the line. Residents can dynamically distribute loads in the house to address their energy needs. Or they can fully rely on the energy they generate and, thus, be absolutely independent of their regional grid.
The operation of smart grid relies on a broad range of technology and infrastructure solutions. Smart grid based on IoT and data technologies is prevailing and includes several important components:
- Smart grid sensors and meters. The role of sensor technology is very important because these are the components that help track energy consumption on the consumer side. Sensors in smart appliances continuously create and report status data to enable monitoring and control. Smart meters collect energy use data and show the full picture of energy consumption in the house, including loads and estimated cost.
- Automated distribution. Advanced distribution systems use real-time data to dynamically respond to the changes in load, detect overload and correct power distribution to enable both safety and economic savings. This is an example of how a smart grid using IoT enables automation.
- Charging stations and smart storage. The role of energy storage and charging stations in continuously increasing. Not only do these technologies allow households to safely go off-grid in cases of outages or accidents. They also reflect the growing demand for independent residential renewable systems.
The role of IoT in smart grid is crucial. Internet of Things is in large part the enabler of smart grid as its technological and infrastructural components are largely IoT-based.
Connected devices, appliances, hubs

The data on energy consumption comes from sensor-enabled IoT devices, appliances and hubs that control a smart house or any other connected space. This data is then used to analyze electricity usage, calculate the cost, remotely control appliances, make decisions on load distribution, detect malfunctions.
IoT-based process automation
Smart grid IoT technology is widely used to automate processes and increase efficiency in the supply chain. Producers and destributers:
- Adopt automated metering to monitor energy usage in real-time and dynamically respond to changing demand.
- Use environmental data and IoT technologies in renewable energy to optimize power production and maximize the use of green sources of energy.
- Monitor grid load and adopt data-driven strategy to minimize the risks of outages or overloads.
Predictive maintenance
Predictive maintenance is one of the most important use cases for smart grid IoT applications for power plants, energy distributors and utilities. Operations on the upstream and downstream sides are built on the use of expensive equipment and infrastructure. Using intelligent grid technology for monitoring and energy grid management allows stakeholders to better control their assets, predict wear or malfunction and implement timely maintenance.
Real-time data analytics and visualization
As mentioned above, the role of big data in smart grid operation is very significant. Thanks to processing, sorting, cleaning, analysis and visualization of IoT data, stakeholders gain important insights about the processes in the supply chain from the moment the energy is produced to the point it is consumed by an end-user. Big data applications enable automation, management, problem detection and prediction in a smart energy grid.
Advanced algorithms
Applications based on machine learning are already common in the IoT market, and IoT smart energy grid is not an exception. We know for a fact that machine learning is good at working with massive datum sets. It helps better understand and use big data, identify trends, make predictions. Therefore, the use of advanced algorithms to analyze IoT data created in the smart grid supply chain is another way to make it more efficient.
Here are some successful examples of the use of IoT in smart grid, from the national level to startup solutions for households.
- Germany has integrated IoT infrastructure and technology solutions to implement a smart grid project in Mannheim. This project enabled the broad adoption of renewable energy and allowed to coordinate energy consumption and production in the city.
- Lumin energy management platform is a good example of IoT application in smart grid which enables cost savings, reduced emissions and easier adoption of green energy at the same time. The company offers a smart panel and data analytics tools to optimize storage, manage electricity consumption and facilitate the integration of PV systems in houses.
- Schneider Electric offers a set of connected solutions for implementing solar power for homes. The company can equip a household with PV systems, monitoring and management tools to go fully off-grid or generate and convert solar energy to partially cover the household’s demand.
- Cisco is one of the leaders among Internet of Things smart grid enablers. The company together with several partners helps different players on the upstream and downstream side to bring in connected technology and enhance grid operations. Among their success stories is the modernization of BC Hydro. Cisco helped the utility provider increase efficiency and reliability using smart metering and advanced analytics technologies.
- Siemens has a large share of solutions for smart grid in IoT portfolio. The company offers a range of software and infrastructure solutions for energy intelligence. One of their clients, a German electrical wholesaler Rexel, implemented a large retrofit project and integrated a power monitoring system by Siemens for energy metering and analytics.
At Digiteum, we know about the technologies used in IoT power grid and energy-efficient systems first-hand. We have experience in building software for IoT and green energy projects, including designing and developing software and middleware for IoT energy monitoring system, creating data analytics and visualization tools, advanced algorithms for device identification, and more.
Are you working on a smart grid project and looking for an experienced team of software designers and engineers? Check our portfolio, IoT software development services and other capabilities and contact us to start a conversation.
Contact Digiteum