10 Benefits of Smart Energy Management using IoT (Internet of Things)
IoT drives process automation and operational efficiency in many industries — healthcare, retail, manufacturing, energy, logistics. IoT applications in energy sector gain particular attention from consumers, businesses and even governments. Apart from numerous benefits to the electric power supply chain, IoT energy management systems give way to new smarter grids and promise unprecedented savings, improved security and enhanced efficiency.
Let’s find out how Internet of Things and energy efficiency are connected, look into the key benefits of using Internet of Things in energy sector and several available solutions in this market.
Need help with software development for IoT in energy sector? Check our IoT software development services and contact our team to talk about your needs.
Contact Digiteum

As we mentioned earlier, IoT-based energy management systems provide a wide range of benefits for every part of the electricity supply chain, including electric utilities, distributors, and consumers. Here are the 10 key benefits of using IoT technology for custom energy software development.
Reduce energy spending
Economic benefit is one of the major reasons why companies and governments are exploring the capabilities of IoT for energy efficiency. Smart metering, real-time power usage monitoring and data-driven predictions help everyone in the supply chain better control spending and investment and eliminate waste.
Minimize carbon emission
Energy sector has been going through tremendous changes to keep up with emerging regulations generally aimed at reducing emissions. Companies increasingly integrate IoT energy consumption and management software and other solutions to their operations to decrease their carbon footprint — optimize the use of resources, measure and analyze their environmental impact and build future-oriented strategies focused on net-zero goals.
Better comply with regulations
Not only do companies leverage IoT for energy management in everyday operations but also use analytics tools to see how they comply with current environmental regulations. Modern SaaS platforms provide specific analytics tools that show if customers qualify for industry certifications, incentives and programs.
Integrate green energy
Both downstream and upstream professionals in this sector understand that transition towards green energy is inevitable and make steps towards integrating clean energy strategy into their operations. Using energy monitoring sensors, performance and power consumption data, utilities, for instance, better understand how to maximize the use of renewables in their services and adopt energy conservation strategies.
Optimize asset maintenance
Advantages of Internet of Things for energy industry are abundant and go beyond energy efficiency. Similar to using connected technology in industrial facilities, sensors and data analytics can be used to monitor the condition and performance of machinery and equipment on power plants and distribution networks not to mention the wide adoption of IoT in renewable energy sector (solar fields, dams, wind farms, etc.).
Automate processes
Utilities, power distributors and producers invest in modernization to do more than just smart energy management using IoT. They rebuild their operations to drive automation and optimize labor costs. Using IoT-based monitoring systems, for example, producers automate costly on-site asset management and improve maintenance operations. Utilities rely on power consumption data to automate dynamic pricing calculations.
Cut operational expenses
Automation, optimized workforce and effective asset maintenance all together lead to a significant decrease in operational expenses. The adoption of advanced analytics software alone is estimated to cut down on 90% of the time and effort spent on energy analysis, reporting and calculation.
Predict consumption and spending and plan accordingly
If you pair a system for energy management with IoT data and machine learning algorithms, you get a tool to predict energy consumption in the future. These insights allow energy companies to build a data-driven strategy for energy production and help utilities improve their demand-based pricing models. As a result, key stakeholders in the supply chain work out an effective strategy for energy conservation using IoT data and machine intelligence.
Identify malfunctions and prevent them
Another good reason to use predictive algorithms is to identify possible issues in operations even before they happen and take preventive actions instead of dealing with real damage. Energy providers, for example, can use insights on energy consumption trends to foresee load spikes and introduce incentives to balance demand and prevent overloads.
Effectively address outages and accidents
In cases when a predictive approach can’t be applied — accidents or blackouts by natural causes — smart analytics systems are still widely used to minimize damage and resolve issues. Using sensor data, for instance, operators can locate the problem, find out how severe the damage is and create an effective repair plan.
These are the key, however, not only benefits of the energy management system and IoT adoption in this sector. Let’s go through 5 major applications of energy control and IoT power management systems for different categories of users.
Working on an IoT-based energy management system? We have tech specialists with experience in designing and building embedded systems and IoT software for energy management. If you are looking for skilled engineers to help you develop a scalable and reliable IoT-based power management system faster, fill in our quick contact form and tell us about your project.
Contact Digiteum
1. Smart light, temperature, air condition control
The most obvious way to save energy is to cut down on wasting it. Smart lighting, learning thermostats and a new generation of sensor-based HVAC systems are designed to automatically maintain the perfect conditions in spaces and keep energy use at the optimum level.
Equipped with different sensors (light, movement, humidity, CO2 level, etc.) these systems can dynamically adjust the regimes depending on the changing conditions and avoid using energy in vain.
IoT energy efficiency applications are abundant and easily available to consumers. Think of smart lighting that dims depending on the amount of daylight available in the room and automatically turns off once the room is empty. Or learning thermostats that precool the space before the heat comes to avoid using expensive energy at the peak load time.
Current by General Electric is an excellent example of an Internet of Things energy management solution. The Company provides a set of LED light, sensors, controls and analytics tools to create a smart energy infrastructure in industrial and commercial spaces, including factories, stores and the whole cities. The solution is promised to save up to 70% on electric bills.
Philips Hue and Ecobee 4 are lighting and smart thermostat solutions that provide enormous savings for households. Philips Hue family of products includes outdoor and indoor LED lighting which adjusts to people’s preferences and routines and uses 85% less energy than traditional bulbs. Ecobee 4 thermostat is another great example of an Internet of Things energy efficiency application. This smart thermostat automatically cuts down on the use of energy when it’s the most expensive thus providing an additional 33% energy saving.
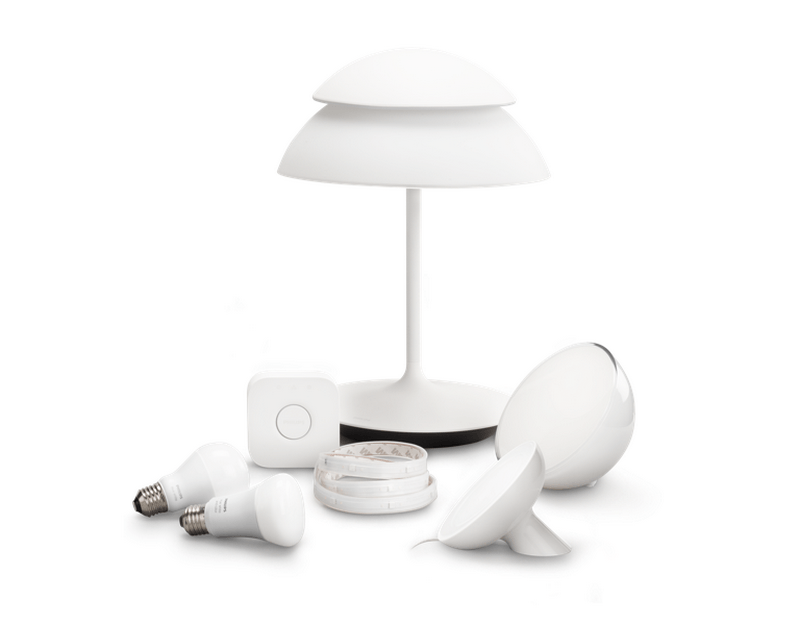

Image credit: Philips Hue
2. Energy management systems
Smart bulbs and thermostats are popular home automation tools. Increasing demand on this market proves that the integration of even the most basic IoT energy control tools can provide viable benefits and enable savings without much effort on the user’s side.
Digital energy management systems include sensors, meters, controls, analytics tools, and other IoT applications in the energy sector that enable users — households, businesses, energy professionals, communities, governments — to monitor, manage and control processes, assets, and resources in the supply chain.
IoT smart energy management market is estimated to reach $9.3 billion by 2023.
Smart meters, for example, monitor power consumption in real-time, dynamically calculate spending and share data between end-users and utility companies. This data helps suppliers tailor demand-response programs and adjust pricing. Residents, in turn, can control their electricity usage at a granular level using applications, respond to load changes, limit wasting energy.
Sensor-enabled assets, be it heavy machinery on a plant or a household boiler, can continuously report load and predict overheating, risks of damage or outage on the line. In the case of the plant’s equipment — motors, for example, — prevented damage results in serious savings. Using tracking data analytics, management can find the right balance between optimum performance of the equipment, wear and energy use and ensure a long life for the assets.
Sensital‘s Internet of Things energy management system for industrial and commercial spaces is a good example. Using the datum coming from a network of sensors and meters on-site, the solution provides saving measures to optimize the use of energy and maximize productivity.
Sense is a smart metering system for households. It is connected to a regular electric panel to enable residents to gain full control and visibility in their energy usage and proactively participate in energy management.
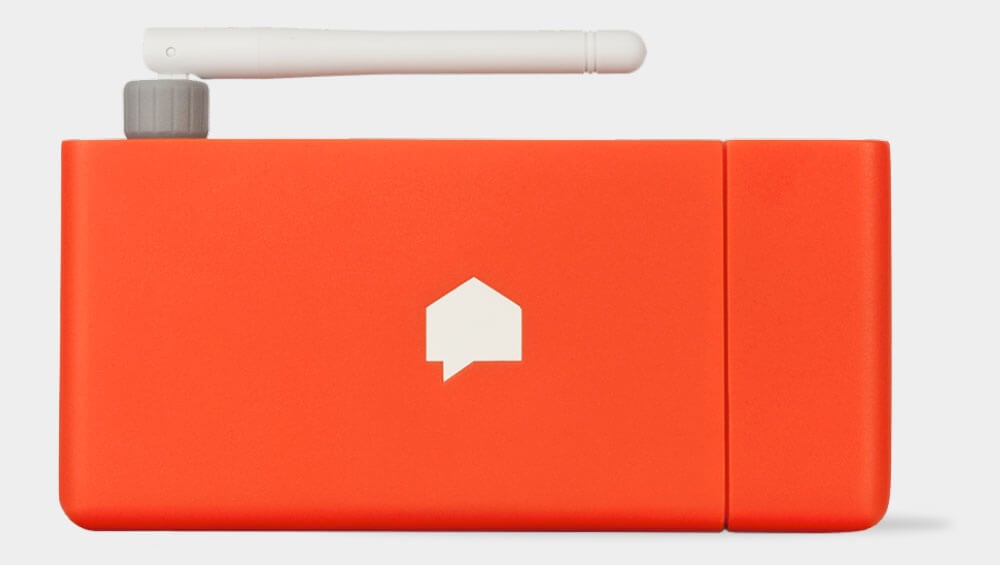

Image credit: Sense
3. Green energy solutions
Today, we can use Internet of Things for energy management and expanding the adoption of green energy. IoT-based residential solar systems and wind turbines offer free power to partially or fully fulfill a household’s energy demand.
In the first case, residential renewables cut the average energy bill by 50%. In the second case, this number goes up to 100% and allows a household go completely off-grid.
Not only does the adoption of residential renewable power systems help save energy, but also to reduces carbon footprint and contributes to the environment conservation initiative.
Schneider Electric solutions for households and smart buildings are a great example of using IoT in energy management. The company provides a wide range of industrial, commercial, and residential solar solutions, as well as full-scale PV power plants.
Each solution consists of a set of connected hardware such as gateways, power banks, batteries, meters and converters and software for real-time power monitoring and control. Depending on the purpose and configuration, Schneider Electric’s solutions enable full energy independence, efficient backup or hybridization with other power sources.
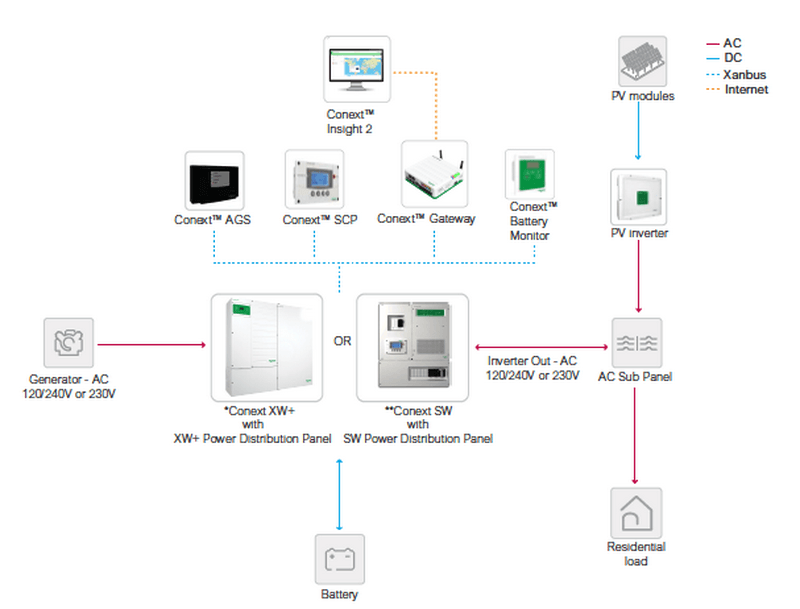
Image credit: Schneider Electric
4. Energy storage
Energy storage is a whole new market. It is gaining attention in the wake of the recent trends in smart home sector and the growing role of IoT in smart city concept.
In general, storage allows consumers to maintain energy independence and resilience in the case of an outage or other problem on the line. Smart storage enables controlled and efficient energy backup and gives residents management functions.
Using smart storage, residents can make informed decisions on the loads and choose which loads should be protected, how much energy should be spent in the off-grid mode and where.
Moreover, by integrating smart storage solutions, the adopters of solar and other renewables can better manage the clean energy they generate, control the surplus and ensure maximized performance for their power network.
In other words, energy storage is the IoT energy-saving application that allows household owners to both control the source and volume of their energy and dynamically respond to issues on the line.
Lumin Energy Management Platform is an example of a smart storage and electricity metering solution which provides customers with monitoring and management capabilities and simplifies the adoption of solar in residential buildings.

5. Connected stations, plants, solar and wind fields
Another application of IoT for saving energy is focused on optimizing power production operations. Stations, plants, solar fields and wind turbines also consume energy, and require maintenance and a wide range of effort and resource-heavy work to keep them running. Using IoT or the Internet of Energy Things in this sector helps maximize performance.
Resource management in Internet of Energy Things implies a complex of measures to optimize the performance of a power grid. It includes using sensors, data analytics, predictive maintenance and other practices.
Read: How IoT is used in smart grid system development
Continuous condition monitoring of equipment and wiring using sensors, for example, prevents overloads and helps maintain a balanced load on the line. Predictive maintenance ensures the timely repair of the equipment and prevents blackouts, accidents and costly downtime.
In some cases, connecting power plants and renewable grids into a network gives consumers a transparent view of where their energy comes from. And with this information, consumers get a choice to use the cleanest source available at the moment.
This is exactly what Whatttime platform offers to people. The nonprofit organization provides technology solutions to enable “automated emission reduction.” In short, the system monitors the network of grids and dynamically shifts to the power source which produces the least emissions at a given time.
With this application of Internet of Things, electric utilities that produce the cleanest energy get more consumers, reduce carbon-heavy energy and ensure better environmental practices.

At Digiteum, we have solid experience in developing software and middleware for Internet of Energy Things. We understand the complexity and costs of adopting IoT energy technology, what it takes to build a viable software product in this sector and how to get it up and running.
One of our clients, a fast-growing US-based energy company, asked us to develop a complex of middleware, software and data infrastructure solutions for an innovative IoT system for household energy management and storage. Our IoT development team has been working on the system for more than a year before it was rolled out to the market and immediately got spotted by specialists in the clean energy space. Learn about this success story in the case study — Internet of Things energy consumption management.
Ready to start your project? Contact our team and tell us about your project.
Contact Digiteum
FAQ
- Reduce energy spending
- Minimize carbon emission and drive sustainability
- Better comply with regulations
- Integrate green energy
- Optimize asset maintenance
- Automate processes
- Cut operational expenses
- Predict consumption and spending and plan accordingly
- Identify malfunctions and prevent them
- Effectively address outages and accidents